Organic GardeningInsect Glossary I-L
Organic gardening Insectipedia insect glossary I-L is a free resource of garden insects, insect terms, and helpful information.
The spread or swarm of insects in or over a plant or crop in a
troublesome or harmful manner.
Insecticidal soap sprays are a safe and affective on organic
garden vegetables, fruit and nut trees, flowers, trees and shrubs.
Only certain soaps have insecticidal properties; detergents
are not soaps. Insecticidal soap sprays are made of fatty acids derived
from plant and animal sources. When sprayed on certain pest it destroys
the insect's membranes. There is no pesticide residue to contaminate
the environment. The sprays are harmless to humans and little effect on
beneficial insects.
Insecticidal soap sprays are available commercially.
Instar is the stage in the life of an insect, or arthropod,
between two successive molts.
Top of Insect Glossary
For more information, select Intercropping
Guidelines or Intercropping
Matrix.
Intercropping is the mixing of different plants in the same
planting to reduce insect pests in your organic garden. Intercropping
allows for greater plant diversity, which reduces pests in a variety of
ways, including:
Chemical Repellent - These plants provide odors that confuse
and ward off pests. This works best in intensive intercropping.
Parasitic Wasp Host Plant - These are plants that provide food
and shelter for parasitic
wasps as they search for pests.
Parasitic Wasp Increase - These plants attract parasitic wasps
as a food source from either the plant or the pests.
Physical Interference - These plants "get in the way"
of the pest as either a physical barrier or a life cycle interference.
Predator Increase. These plants act as a food source or
breeding ground for beneficial insects as they search out for pests.
Trap Crop - Trap cropping encourages pests to congregate,
which makes it easier for beneficial insects to prey and for handpicking.
Visual Masking - These plants provide a visual mask that
either may confuse the pest or concealed the main crop.
Intercropping
Guidelines
Guidelines for intercropping
with plants that repel insects:
1. Intercropping is not an exact science. What might work for
one gardener may not work for another. A degree of success depends on
your soil (see healthy
soil), skill level, knowledge, climate, and Ecoregion.
2. Always experiment. Learn from your own experience what
works and what doesn't.
3. Don't interplant when space is limited.
4. Look for reactions from your crops such as stunted
growth or poor yields. Some plants may release chemicals that have
adverse effects on others.
5. Don't allow the intercropped plant to out-compete for
water, sun, or nutrients.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Organisms lining inside other organisms, such as insects. For
example, the larvae of the Tachinid
Fly are an internal parasite to beetles, grasshoppers, and
Caterpillars, as well as a few others.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Iron is important in building the chlorophyll molecule, and it
is therefore important to photosynthesis. Crops such as the cabbage
family, spinach, beets, tomatoes, and beans demand a good supply of
iron. Like manganese,
iron deficiencies are most likely to occur in cool, moist springtime
conditions. Deficiencies will also occur in soils with a pH
of 7.5 or higher.
It is common to see high levels of iron and manganese in
waterlogged soils lacking sufficient oxygen. Once the soil drains
sufficiently and air is reintroduced into the soil environment, the
levels generally decrease.
The labium is located behind the maxilla and acts as a guide
for the food.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
The labrum is located just above the mouthparts and is a small
plate-like "upper lip."
Probably the best-known and most valued Aphid and Scale predator
is the Lady Beetle (Ladybird or Ladybug). The adult Lady Beetle is
usually orange, reddish, or yellow with very distinct black spots.
There are a few species with no spots. The female deposits her
eggs singly or in groups on foliage that is infested with Aphids or
Scale insects. The larva is long and slender, usually gray with black,
red, green, and blue spots. The larvae are very active and feed on the
Aphids and Scale. Lady Beetles congregate in large numbers in the Fall
to overwinter
beneath logs, stones, leaves, or other surface debris.
Lady Beetles can easily be obtained commercially.
The Lady Beetles found in this knowledge base are:
Lady Beetle
(Cycloneda sp.)
Lady
Beetle (Hippodamia convergens)
Lady
Beetle (Olla abdominalis)
Lady
Beetle (Rodolia cardinalis)
Lady
Beetle (Stethorus picipes)
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
VIEW IMAGES OF LARVAE
A larva is the immature, wingless form of insect that hatches
from an egg. It grows as it passes through many molts, and
then transforms into a pupa
or chrysalis from which an adult emerges.
There are many varieties of Leafhoppers, or insects belonging
to the Homoptera
order, characterized by slightly thickened, and often marked with color
patterns match those of Head and thorax.
Adults and nymphs
have an odd habit of running sidewise when the plants are disturbed.
The adults hop or fly away. They damage they cause by sucking the
juices and injecting salivary substances that block conductive system.
discoloring of the leaves and stunted
growth results. Both Spittlebugs and Leafhoppers are vectors (carriers
that transmit) of viruses of Pierce's disease, Aster yellows, and other
plant disease.
Controls that can be are forceful jet of water, covering
plants with nylon
netting, dusting lightly with Diatomaceous
earth, or dormant-oil
spray.
The Leafhoppers found in this knowledge base are:
Beet Leafhopper
Blue Sharpshooter
Glassy-winged
Sharpshooter
Potato Leafhopper
Redbanded
Leafhopper
Spittlebugs/Froghoppers
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
It's important to look for signs of insect attack. The signs
may show up as leaf or foliage damage. Types of leaf damage are:
1. Leaves chewed from outside edge
2. Leaves with speckles or speckles and may be chewed

3. Leaves are chewed in the inside

4. Leaves may be wilting and discolored

5. Leaves are curling
6. Leaves are skeletonized

7. Leaves have tunnel marks

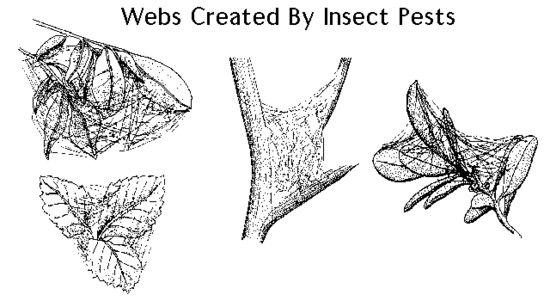
8. Leaves may be surrounded in webs
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Bean Pea
Peanut Soybean
A legume is a plant with two seed leaves, such as an herb,
shrub, or tree having fruits that bear nodules on the roots that
contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and is an important food and forage
plant.
A legume is a plant with two seed leaves, such as an herb,
shrub, or tree having fruits that bear nodules on the roots that
contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria, and is an important food and forage
plant.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Lepidoptera
The order Lepidoptera is the second largest order of Insects
and includes the butterflies and moths.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Life cycle is the series of stages in form and functional
activity through which an insect passes in its complete lifetime.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Those crops that use a minimal amount of nutrients from the
soil such as nitrogen.
Examples of light feeders:
Beets Carrots Garlic Onions Parsnips Potatoes Radishes Turnips
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
A lightweight crystalline thermoplastic that is resistant to
chemicals and moisture, and possesses good insulation properties. It
transmits 85% to 95%
of sunlight can be used to protect plants from insect attack. Easily
obtained from most hardware stores.
Do not use if temperatures are consistently over
80 degrees.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Limestone is a rock that is formed from organic remains, such
as shells and coral, consisting mainly of calcium carbonate and
produces lime when burned. Lime is very effective in the fight against
snails and slugs.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Plant and other organic matter scattered about in disorder. In
gardens, litter can consist of prunings, leaves, or weeds that have not
been cleared from the area.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Lodging is when Wheat is heavy and high yielding, and the wind
knocks it flat to the ground. When this occurs, it makes harvesting
very difficult. Too much nitrogen, which produces fast, rank growth and
lack of potassium, may also cause lodging.
Top of Insect Glossary I-L
Luciferin is a pigment found in luminescent organisms, such as
fireflies, which furnishes practically heatless light as it is oxidized.
Back to the top
Retun from Insect Glossary I-L to Insectipedia
Enjoy this page? Please pay it forward. Here's how...
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment,
your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.







