Organic GardeningInsect Glossary E-H
Organic gardening Insectipedia insect glossary E-H is a free resource of garden insects, insect terms, and helpful information.
If there are only a few pests present, probe the borehole with
wire to kill them. Remove and burn all infested plants and branches in
the spring, before the adult emerges to lay more eggs.
Cultivation
tends to eliminate over wintering insects and destroys eggs.
Crop rotation
and varying the planting dates to offset borer attacks significantly
reduces these pests.
If the Borers
have infested Vegetable
crops, destroy all plants immediately after harvest.
Poisons and repellents are ineffective against borers unless
it is applied during the time the adults are laying eggs or when the
adults are emerging from the eggs. Prevention is the best solution.
An elliptical shape is a uniform oval.
Top of Insect Glossary
The elytra are the anterior or forward most, wings in beetles
and other insects that serve as protection for the posterior, or rear
most, pair of functional wings.
CAUTION: The use of the following
natural insecticides should be used only when control tactics have
failed.
1. Bacillus
thuringiensis
2. Milky
Spore Disease
3. Diatomaceous
earth
4. Pyrethrum
5. Sabadilla
6. Rotenone
7. Ryania
8. Tobacco
dust
Top of Insect Glossary
Excreta is the waste matter from an animal and other living
organisms.
To fabricate is to make, build or construct something, in this
case a trap. In this instance the word fabricate is very appropriate
because it can also means to make up for the purpose of deception. That
is exactly what we are doing when we are making, or fabricating, a trap
for insects.
Top of Glossary E-H
The femur houses the powerful tibiae muscles that are used for
jumping. It may also be used for locomotion and sound production.
A firefly is a nocturnal
winged beetle that produces a bright soft intermittent light by
oxidizing luciferin
for courtship purposes. However, not all species of fireflies have
light organs.
The Firefly
is a natural predator of Slugs and Snails.
There are some California species where the female glows but
the winged males don't. They usually range about 1/4 to 1/2 inches
long, males have soft elongated dark wing covers, and the females are
flightless. Females are often called glowworms. eggs are laid on the
ground and produce larva that prey on snails. The single generation
produced each year hibernate and produce the adult in the summer. They
can be found throughout the United States and Southern Canada in open
meadows and gardens.
The outer most part of the antenna, usually divided into many
subsegments. The divided flagellum is joined together by membranes so
that it can be flexible.
Fleshy Fruits (members of the Solanacea)
Eggplant Ground-cherry
Pepper Tomato
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
The decorative parts of plants, such as leaves, flowers, and
branches.
The success of insects as a terrestrial invertebrate is partly
due to their flying capability. Generally, adult insects have two pairs
of wings articulating with the thorax. The forewings are often hardened
and are used to protect the hind wings.
In various insect groups, the wings are modified for sound
production even though they are no longer used for flight.
The central area on the front of the head. Muscles run from
this area to the other parts of the head.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
It is important to look for signs of insect attack. The signs
may show up as fruit damage.
Types of fruit damage are:
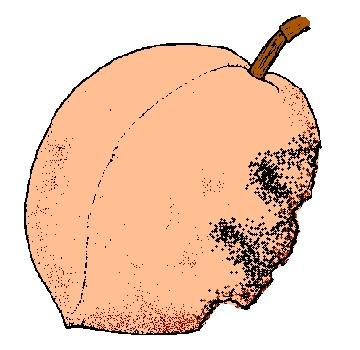
1. Fruit is blemished - beyond recovery
2. Fruit has residue - sawdust-like or gummy
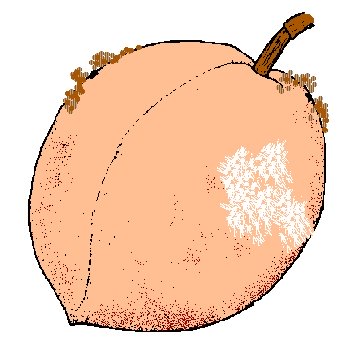
3. Fruit is deformed
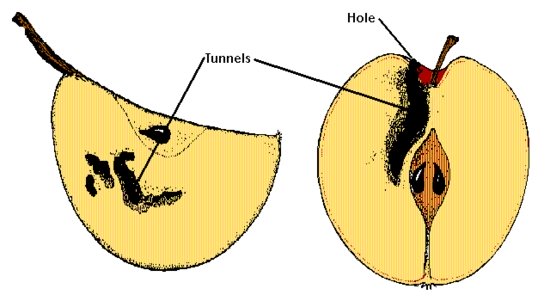
4. Fruit has holes and tunnels inside
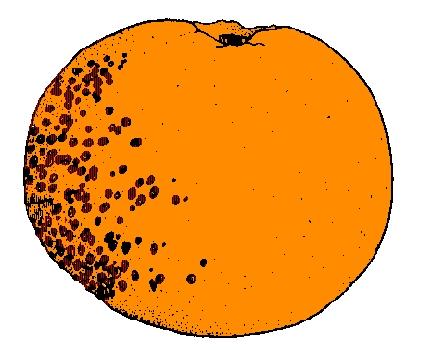
5. Fruit is pitted
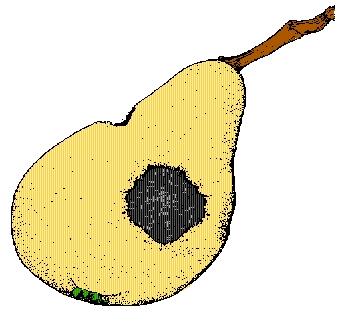
6. Fruit is damaged with mold
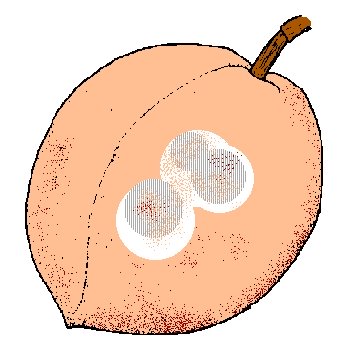
7. Fruit has puncture marks
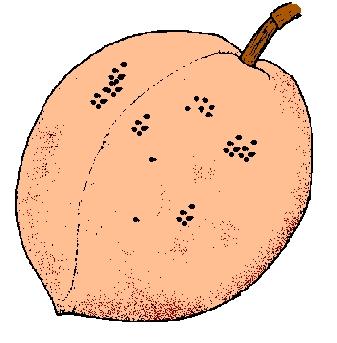
8. Fruit has inflamed areas
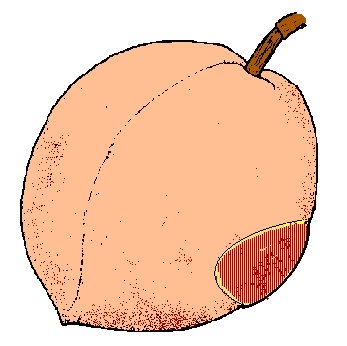
9. Fruit is chewed
Fungi is a term for a major group of fungus which is a
saprophytic or parasitic
lower plant form that lacks chlorophyll and includes mildews, molds,
mushrooms, rusts, smuts
and yeasts.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Gall is the swelling of plant tissue, which is usually caused
by fungi
or insect parasites. Galling sometimes forms an important source of
tannin.
Some orderly method of grouping fruits and vegetables is
necessary to present the knowledge orderly and eliminate repetition.
Fruits and vegetable used throughout the world number in the thousands.
Therefore, some system of classification
is essential.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
A garlic spray usually consists of a diluted garlic-clove
juice or powdered garlic extracts. Garlic sprays have antibiotic
properties that are useful in the fight against bacteria and fungi, such
as downy mildew of cucumber, downy mildew of radish, cucumber scab,
bean rust, bean anthracnose, and early blight of tomato, brown rot of
stone fruits, annular leaf spot of cucumber, and bacterial blight of
beans.
The lateral area (cheek) of the head beneath the eyes is
called the gena.
Barley Millet
Oats Rice
Rye Wheat
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Unripened fruit. Usually green in color and smaller than the
mature size.
A green manure crop is a cover crop that is planted and grown
for tilling under to improve the soil or harvested and used as compost
material. For example, winter cover crops of Rye or Vetch are excellent
soil builders. Cover crops have many advantages, such as adding
nitrogen to the soil, mobilizing minerals and increasing organic matter
to improve fertility, conserving the soils nutrients by reducing what
is lost during leaching, replacing some of what is lost during erosion,
and generally improves the soils physical condition of plant nutrients.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Ground Beetles belong to the Coleoptera
order. All for the most part are beneficial
insects. Mainly black in color, though many are brilliantly
colored or enhanced by iridescent hues. They have long legs
and with Tibia
spurs, and can run rapidly. They are flattened in shape with a
distinguished thorax,
usually narrower than the abdomen.
The eyes are large (except for a few cave species). The eggs are
normally laid in the soil. When full grown the larvae pupate in
the soil.
Mostly nocturnal,
they may be found under rocks or debris in
the daytime. They fiercely feed on Slugs,
Snails, Cutworms, Caterpillars, and larvae of Beetle pests.
Mostly 20,000 Ground Beetles have been identified. Their
identification is hard, because they so closely resemble each other.
The Ground Beetles found in this knowledge base are:
Fiery Hunter
Fiery Searcher
Ground Beetle
Tiger Beetle
Rove Beetle
A grub is a soft-bodied worm-like larva of an
insect, usually Beetles.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
To handpick is to physically pick by hand as opposed to using
machinery. When handpicking insects, be sure to wear gloves.
Where most insects are harmless to humans, there are some that
can irritate the skin.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Hand picking and destroying them whenever they are found. For
at least two weeks, spend each night with a flashlight and a bucket of
diluted soapy
water, handpicking
the Slugs and Snails and dropping them into the bucket. Children love
this activity.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Predaceous
and Scavengers. May sometimes be beneficial, feeding on Mites and small
insects.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Normally about 90% of the time insects will only attack
unhealthy plants. Just as humans who are healthy are less susceptible
to disease, so are healthy plants that are on a good diet less
susceptible to disease and insect attack. The first step in insect
control is to provide your plants with a healthy soil. Your organic
garden soil needs your energy. We must attack the problem not the
symptom (insects).
Here are some elements to consider in establishing a healthy
soil:
1. Are the proper plant nutrients available in the soil? Are
you putting back that which you are taking out?
2. Use only organic
fertilizers instead of chemical or petroleum based
fertilizers.
3. Is the soil pH
within the limits of the crops being grown?
4. Is the soil being dug and cultivated properly? Rototilling
compacts the soil six to eight inches below the surface, which stresses
many crops.
5. How are you watering the crops? Too much? Too Little?
6. Is weeding being maintained effectively?
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Those crops that extract large amount of nutrients from the
soil such as nitrogen.
Examples of heavy feeders:
Corn Fruit trees Melons Parsley Pumpkins Tomatoes
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Those crops that fix nitrogen back into the soil.
Examples of heavy givers:
Acacias
Alders
Alfalfa
Beans
Black
Locust
Ceanothus
Peas
Soybeans
Vetch
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
hemiptera
Members of the Hemiptera are distinguished from all other
insects by both adults and nymphs having a proboscis that includes a
salivary channel as well as a food channel. The proboscis is usually
specialized to suck the juices from various parts of plants, including
seeds, although some species are predatory (on arthropods and sometimes
small animals), and a few are adapted to suck blood from mammals. -
Wikipedia.com
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Hibernation refers to the passing of winter in a torpid or
resting state, or to become dormant or inactive.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Homoptera/Heteroptera

Members of the "Heteroptera" are typically called "true bugs".
The name heteroptera comes from their forewings having both membranous
and hard portions. It is also essentially this same feature which gives
the order its name, hemiptera, coming from the Greek for half-wing.
Members of the Hemiptera are distinguished from all other insects by
both adults and nymphs having a proboscis that includes a salivary
channel as well as a food channel. The proboscis is usually specialized
to suck the juices from various parts of plants, including seeds,
although some species are predatory (on arthropods and sometimes small
animals), and a few are adapted to suck blood from mammals. In
addition, the space between the overlapping wings in the members of
this order forms a triangular shape near the head which is commonly
used to identify a true bug. -Wikipedia.com
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Anal secretions of Aphids and other Homoptera
consisting largely of water and sugars.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
One of the two major types of development where the larvae do
not resemble the adults and a pupal stage occurs.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
When Leafhoppers
feed on plants by inserting their piercing mouthparts into leaves to
suck out the nutritious leaf sap, they can damage the leaf by
interfering with the fluid conduction within the leaf causing a browned
area called hopper burn.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
A host plant is a plant that provides lodgment (shelter or
accommodations) to an insect.
Top of Insect Glossary E-H
Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is one of the larger orders of
insects, comprising the sawflies,
wasps, bees, and ants. The
name refers to the membranous wings of the insects, and is derived from
the Ancient Greek. The hindwings are connected to the forewings by a
series of hooks called hamuli. Females typically have a special
ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or otherwise inaccessible
places, often modified into a stinger. The young develop through
complete metamorphosis - that is, they have a worm-like larval stage
and an inactive pupal stage before they mature. -Wikipedia
Back to the top
Retun from Insect Glossary E-H to Insectipedia
Enjoy this page? Please pay it forward. Here's how...
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment,
your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.









